- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
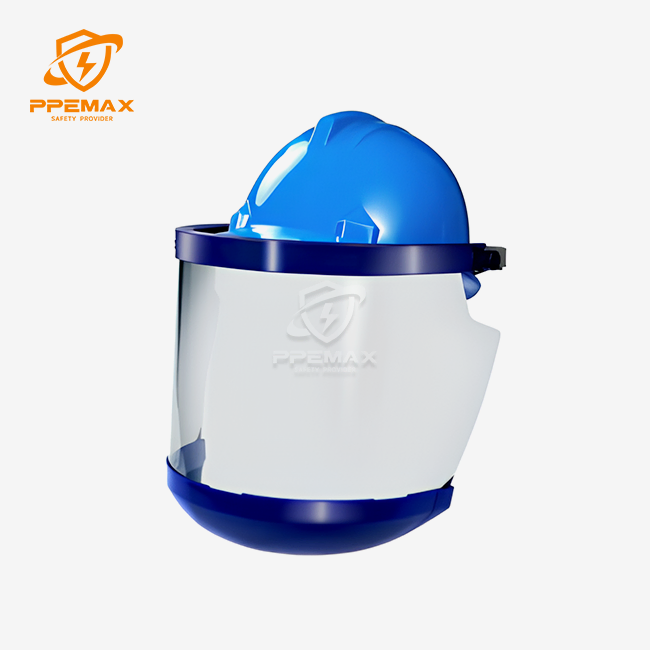
Welding Face Shield Materials: Polycarbonate vs Acrylic
Selecting the appropriate lens material for a Welding Face Shield is one of the most critical decisions affecting welder safety, visibility, and long-term equipment costs. The two primary materials dominating the protective equipment market—polycarbonate and acrylic—offer distinctly different performance characteristics that directly impact protection levels, durability, and optical quality. While both materials provide essential eye and face protection against welding hazards, understanding their unique properties helps safety managers and welders make informed choices aligned with specific working conditions and budgetary constraints. Polycarbonate has emerged as the industry standard for high-impact welding applications due to its exceptional strength and heat resistance, while acrylic continues to serve in applications where optical clarity is paramount and impact risks are moderate. This comprehensive analysis explores the material science, practical performance differences, and application-specific considerations that determine which Welding Face Shield material best serves your operational needs and safety requirements.
What Are the Key Differences Between Polycarbonate and Acrylic Welding Face Shields?
Impact Resistance and Safety Performance
The main difference between polycarbonate and acrylic Welding Face Shields lies in impact resistance. Polycarbonate offers up to 250 times the strength of glass and about 20 times more than acrylic, making it ideal for high-risk welding where debris and sparks are common. Its molecular structure disperses impact energy, preventing breakage and injury. Xi'An PPE MAX Co., Ltd produces polycarbonate shields that meet ANSI Z87.1-2020 standards, ensuring durability and safety. In contrast, acrylic shields are more brittle and prone to shattering under high impact, limiting their use to light-duty applications where severe hazards are less frequent.
Optical Clarity and Visual Performance
Optical clarity is another key difference between the two materials. Acrylic Welding Face Shields traditionally offer excellent transparency with minimal distortion, ideal for precise welding tasks. However, advances in polycarbonate manufacturing have greatly improved its visual performance, providing clarity close to acrylic while maintaining superior toughness. Xi'An PPE MAX’s polycarbonate shields include anti-fog and scratch-resistant coatings, extending usability. With larger viewing areas like 3.82" × 2.44", they enhance peripheral vision. Welders in low-impact environments may prefer acrylic for slightly clearer views, while those in demanding settings favor polycarbonate for its balance of safety and visibility.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Performance
Polycarbonate Welding Face Shields outperform acrylic in thermal resistance, maintaining shape up to 240°F (115°C), compared to acrylic’s 160°F (70°C). This makes polycarbonate better for high-heat welding, oxy-fuel cutting, and confined spaces with heat buildup. It resists warping, pitting, and surface degradation from sparks, ensuring long-term visibility and protection. Xi'An PPE MAX designs lightweight polycarbonate shields optimized for heat stability in industrial use. While acrylic shields suit cooler, controlled environments, polycarbonate remains the superior choice for heavy-duty welding due to its ability to endure repeated thermal exposure and reduce replacement costs over time.
How Do You Choose the Right Material for Your Welding Face Shield?
Application-Specific Requirements Assessment
Choosing between polycarbonate and acrylic Welding Face Shields depends on the welding process, environment, and hazard exposure. For light-duty MIG or TIG welding in controlled conditions, either may suffice, allowing cost to guide the choice. However, heavy industrial work such as shipbuilding or steel fabrication requires polycarbonate for its superior impact and heat resistance. Polycarbonate also blocks more UV radiation and withstands rough handling better than acrylic. In contrast, acrylic suits precision welding in clean, low-impact environments where visual clarity is critical. When welders perform multiple tasks like grinding or cutting, polycarbonate remains the safer, more versatile option.
Cost Considerations and Long-Term Value
While acrylic Welding Face Shields cost less upfront, polycarbonate models often deliver greater long-term value. Acrylic shields may be 20–30% cheaper, but their brittleness leads to frequent replacement and downtime. Polycarbonate shields last significantly longer, reducing total ownership costs and improving productivity. Xi’An PPE MAX offers durable, hard-coated polycarbonate shields that resist scratches and maintain visibility over time. These performance advantages can offset higher initial costs while lowering injury risks and liability. Standardizing on polycarbonate also simplifies worker training and safety compliance, ensuring consistent protection and reducing administrative and operational expenses across the facility.
Regulatory Compliance and Certification Standards
Compliance with safety standards is essential when selecting Welding Face Shield materials. Both polycarbonate and acrylic can meet ANSI Z87.1-2020 impact standards, but polycarbonate provides a higher safety margin. Xi’An PPE MAX shields are certified under major global standards such as EN 175:1997 and AS/NZS 1338.1:2012, ensuring easy compliance for multinational companies. Industries with strict safety protocols, including aerospace and defense, often require polycarbonate for enhanced reliability. Xi’An PPE MAX’s auto-darkening shields feature rapid 1/25,000-second response times and shade ranges of 9–13 for optimal protection. Polycarbonate’s adaptability also ensures better respirator compatibility, simplifying documentation and audit compliance.
What Features Should You Look for in a Quality Welding Face Shield?
Advanced Protection Technologies
Modern Welding Face Shields integrate advanced safety features beyond basic lens protection. Auto-darkening technology automatically adjusts the lens shade to match arc brightness, improving visibility and efficiency without manual adjustments. Xi’An PPE MAX’s models use solar power with battery backup for consistent performance even in dim environments. A 9–13 adjustable shade range ensures versatility across welding types, while multi-sensor systems enhance arc detection reliability. Grind mode allows light-state operation for non-welding tasks. Lightweight full-face designs (1.2 lbs) offer extended coverage and comfort, providing full protection for the face, neck, and head without causing neck strain during prolonged use.
Ergonomic Design and User Comfort
Comfort is vital for ensuring welders consistently use their Welding Face Shields. Adjustable headgear distributes weight evenly and allows personalized fit, while Xi’An PPE MAX’s 1.2 lb lightweight design reduces fatigue during long shifts. Padding at contact points prevents pressure discomfort, and moisture-wicking materials enhance comfort in hot environments. A wide viewing area (3.82" × 2.44") minimizes excessive head movement and improves precision. Ventilation systems help prevent fogging without compromising protection. Compatibility with respirators, hearing protection, and safety glasses ensures welders maintain full safety compliance while working comfortably and efficiently in demanding industrial settings.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Durability determines long-term safety and cost-efficiency. Scratch-resistant and anti-fog coatings maintain lens clarity and reduce replacements, while easily replaceable components—like lenses and headgear—extend service life. Xi’An PPE MAX provides spare parts and technical support to simplify maintenance. Smooth polycarbonate surfaces resist spatter buildup and are easy to clean, supporting regular hygiene practices. Proper storage, aided by protective cases, prevents UV and heat damage. Modular designs allow easy upgrades, such as replacing auto-darkening cartridges. Reliable warranty coverage and after-sales service distinguish premium Welding Face Shields, ensuring lasting value, consistent protection, and dependable performance in industrial environments.
Conclusion
The choice between polycarbonate and acrylic Welding Face Shields materials ultimately depends on your specific application requirements, with polycarbonate offering superior impact resistance and durability for most industrial welding operations while acrylic serves specialized applications prioritizing optical clarity above all else. Understanding material properties, protection technologies, and ergonomic features ensures your workforce receives optimal safety and comfort.
Partner with PPEMAX for Reliable, Custom Welding Face Shield Solutions
Xi'An PPE MAX Co., Ltd has been a leading PPE supplier since 1956, providing globally trusted protection solutions across 134 countries. Partner with us for end-to-end solutions—from expert OEM manufacturing to building your own brand. Benefit from decades of reliable quality, extensive industry experience, and tailored production capabilities. Where there is welding, there is PPEMAX. Where there is safety risk, there is your PPE provider. Contact us today at bettybing@ppemax.com to discuss your Welding Face Shields needs.
References
1. American National Standards Institute. ANSI Z87.1-2020: Occupational and Educational Personal Eye and Face Protection Devices. American National Standards Institute Publication, 2020.
2. Welding Institute Research. Comparative Analysis of Face Shield Materials in High-Temperature Welding Applications. TWI Technical Journal, 2023.
3. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Criteria for Recommended Standard: Welding, Brazing, and Thermal Cutting. NIOSH Publication Series, 2024.
4. European Committee for Standardization. EN 175:1997: Personal Protection - Equipment for Eye and Face Protection During Welding. CEN Standards Publication, 2022.
5. American Welding Society. Safety in Welding, Cutting, and Allied Processes: Material Selection for Personal Protective Equipment. AWS Safety and Health Fact Sheets, 2023.
6. International Safety Equipment Association. Impact Resistance Testing Protocols for Protective Face Shields in Industrial Applications. ISEA Technical Standards Review, 2024.
Learn about our latest products and discounts through SMS or email